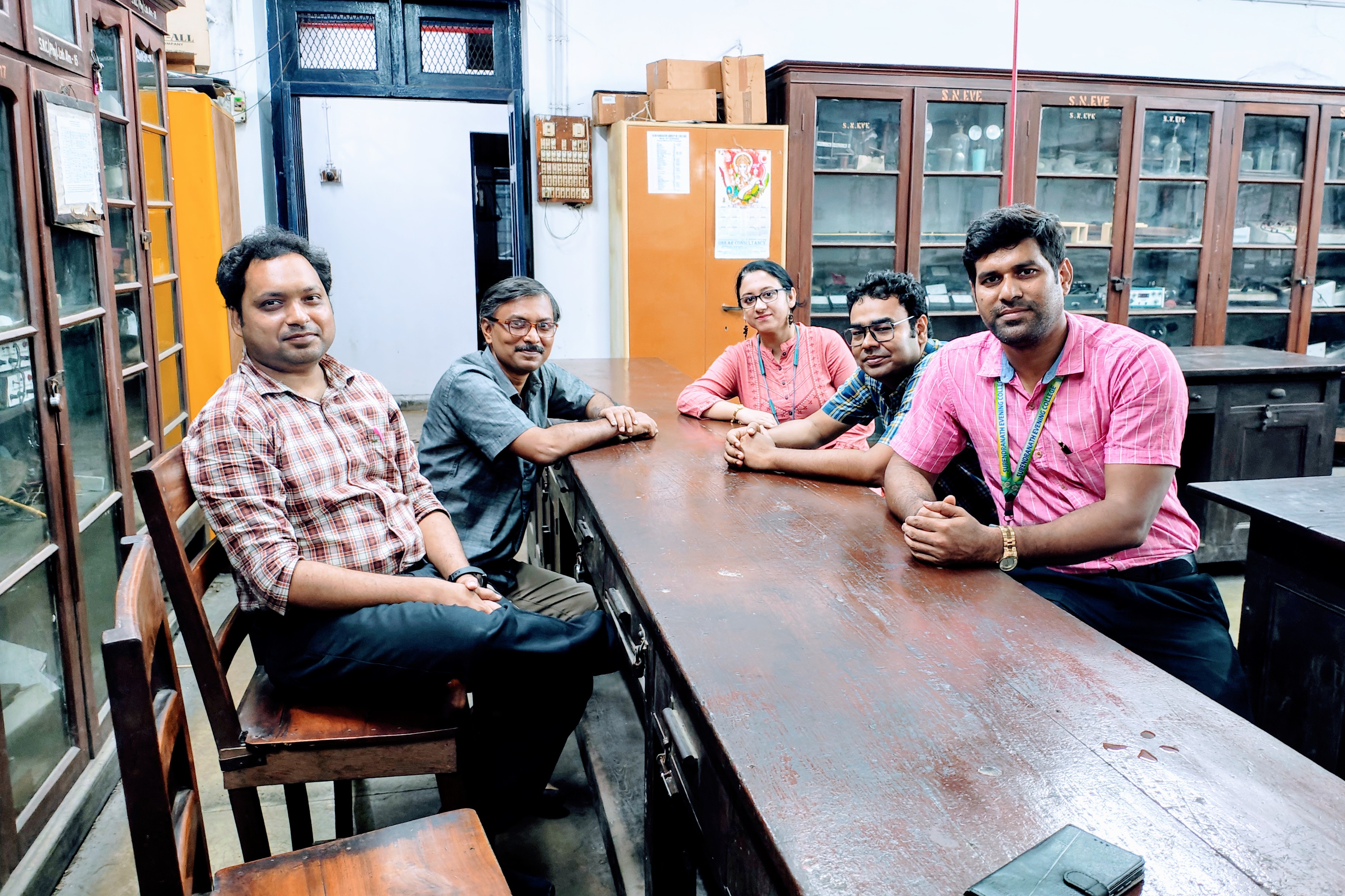
The members of the faculty of the department of physics specialize in topics related to materials science, nanomaterials, coupled nanomaterials, scanning tunneling microscopes, first principle study of 2d magnetic/nonmagnetic materials, nuclear structure and decay, and low energy nuclear astrophysics. The faculty have publications in renowned journals in their respective fields. Presently our department has five faculty members in substantive posts.


It has a separate computer laboratory with computers with the latest hardware configurations and operating systems (Windows and Linux), a LaserJet printer and internet connection through Wi-Fi and LAN.
The department also has a gallery classroom which is equipped with a projector and a whiteboard in addition to a traditional blackboard to facilitate a smooth teaching-learning experience.


The dedicated non-teaching support-staff of our department help in the day-to-day conduct of the classes, as also in the conduct of the practical examinations.
From session 2023-24 onwards, we offer 4 Year B.Sc. Physics (Honours & Honours with Research), and 3 Year B.Sc. Multi-Disciplinary Course (MDC) under the Curriculum and Credit Framework (CCF) of the New Education Policy (NEP).
Also, the department runs courses under the Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) Framework introduced by the UGC for Honours and General students. At present, 4th and 6th Semester classes are under the CBCS scheme.
Please follow the links for the current syllabus:
Sem-I and II PHYSICS syllabus Under CCF-2022:
https://www.caluniv.ac.in/ccf-ug/files/ccf-physics.pdf
Physics syllabus under CBCS 2019:
https://www.caluniv.ac.in/cbcs-ug/ug-files/Physics-14-11-19.pdf
Dr Samit Bhowal
1. Levels in doubly odd 138Pr, G. Gangopadhyay, Samit Bhowal, R. K. Bhowmik,
U. Datta Pramanik, P. Ghosh, A. Goswami, C. Petrache, A. Mukherjee, S. Muralithar,
Rajarshi Raut, M. Saha Sarkar, A. K. Singh, R.P. Singh and S. Bhattacharya, Eur. Phys.
J. A 24, 173 (2005).
2. Study of yrast band in 155Tm, R. Raut, S. Bhowal, S. Ganguly, R. Kshetri, P.
Banerjee, S. Bhattacharya, R. K. Bhowmik, B. Dasmahapatra, G. Gangopadhyay, A.
Mukherjee, S. Muralithar, M.Saha Sarkar, R.P.Singh and A. Goswami, Nucl. Phys. A
791, 1 (2007).
3. High Spin Structure of 35Cl and the sd − fp shell gap, Ritesh Kshetri, M. Saha
Sarkar, Indrani Ray, P. Banerjee, S. Sarkar, Rajarshi Raut, A. Goswami, J. M. Chatterjee,
S. Chattopadhyay, U. Datta Pramanik, A. Mukherjee, C. C. Dey, S. Bhattacharya, B.
Dasmahapatra, Samit Bhowal, G. Gangopadhyay, P. Datta, H.C. Jain, R. K. Bhowmik,
S. Muralithar, R. P. Singh and R. Kumar, Nucl. Phys. A 781, 277 (2007).
4. Energy levels in 141Nd from fusion evaporation study, Samit Bhowal, Chirashree
Lahiri, Rajarshi Raut, Purnima Singh, M. Kumar Raju, A. Goswami, A. K. Singh, S.
Bhattacharya, T. Bhattacharjee, G. Mukherjee, S. Bhattacharya, S. Muralithar, R. K.
Bhowmik, N. Madhavan, R. P. Singh and G. Gangopadhyay, J. Phys. G: Part. Nucl.
Phys 38, 035105 (2011).
5. Development of collective structures over non-collective excitations in 139Nd, Samit
Bhowal, G. Gangopadhyay, C.M. Petrache, I. Ragnarsson, A. K. Singh, S. Bhattacharya,
H. H¨ubel, A. Neußer-Neffgen, A. Al-Khatib, P. Bringel, A. Burger, N. Nenoff, G. Schonwasser,
G. B. Hagemann, B. Herskind, D. R. Jensen, G. Sletten, P. Fallon, A. Gorgen, P.
Bednarczyk, D. Curien, A. Korichi, A. Lopez-Martens, B. V. T. Rao, T. S. Reddy and
Nirmal Singh, Phys. Rev. C 84, 024313 (2011).
6. Evidence for octupole correlation and chiral symmetry breaking in 124Cs, K. Selvakumar, A. K. Singh, Chandan Ghosh, Purnima Singh, A. Gowsami, R. Raut, A. Mukherjee, U. Datta, P. Dutta, S. Roy, G. Gangopadhyay, S. Bhowal, S. Muralithar, R. Kumar, R. P. Singh, and M. Kumar Raju, Phys. Rev. C 92, 064307 (2015).
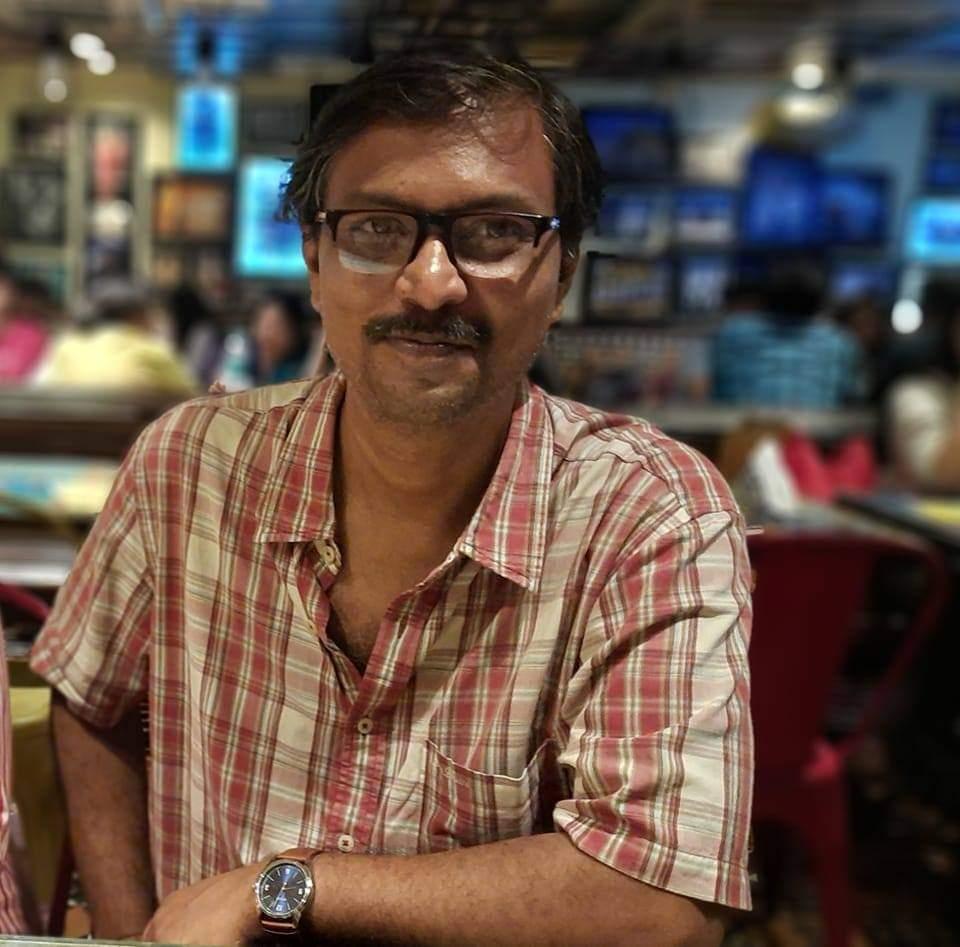
Dr Sanjit Sarkar
1. Understanding of mobility limiting factors in solution grown Al doped ZnO thin film and its low temperature remedy, B Mahapatra, S Sarkar Heliyon 8 (10), e10961
2. Tuned synthesis and designed characterization of graphene oxide thin film, HS Biswas, S Bala, AK Kundu, I Saha, S Poddar, S Sarkar, P Mandal Inorganic Chemistry Communications 139, 109356
3. Fabrication of Graphene-Fe3O4-Polypyrrole based ternary material as an electrode for Pseudocapacitor application, P Mandal, S Bala, S Poddar, S Sarkar, HS Biswas Materials Today: Proceedings 65, 1001-1010
4. Boosting the Supercapacitive performance of ZnO by 3-dimensional conductive wrapping with graphene sheet, A Dutta, S Mishra, SK Saha, S Sarkar, A Guchhait, AJ Akhtar Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials, 1-11.
5. All‐Inorganic Halide Perovskite Nanocrystals: Future Prospects and Challenges to Go Lead Free, S Sarkar physica status solidi (a) 218 (14), 2100185.
6. Synthesis of Graphene Oxide from Hydrogenated Diamond Like Carbon and Protein Immobilization onto It: Characterization and Study of Practical Utility, S Bala, R Bose, S Chaterjee, S Sarkar, I Saha, HS Biswas Journal of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering 9 (01), 32
7. Self-powered highly enhanced broad wavelength (UV to visible) photoresponse of ZnO@ ZnO1− xSx@ ZnS core–shell heterostructures, S Sarkar, AD Mahapatra, D Basak Journal of colloid and interface science 523, 245-253.
8. Core-double shell ZnO/ZnS@ Co 3 O 4 heterostructure as high performance pseudocapacitor, S Sarkar, S Maiti, S Mahanty, D Basak Dalton Transactions 45 (22), 9103-9112.
9. An insight into doping mechanism in Sn–F co-doped transparent conducting ZnO films by correlating structural, electrical and optical properties, A Mallick, S Sarkar, T Ghosh, D Basak Journal of Alloys and Compounds 646, 56-62
10. Self powered highly enhanced dual wavelength ZnO@ CdS core–shell nanorod arrays photodetector: an intelligent pair, S Sarkar, D Basak ACS applied materials & interfaces 7 (30), 16322-16329
11. Understanding of ultraviolet photoresponse properties of ZnO nanorods: effect of nanorod’s size and ambient, S Sarkar, D Basak Sci Lett J 5, 4.
12. Defect mediated highly enhanced ultraviolet emission in P-doped ZnO nanorods, S Sarkar, D Basak RSC Advances 4 (74), 39095-39100
13. A successive photocurrent transient study to probe the sub-band gap electron and hole traps in ZnO nanorods, D Sett, S Sarkar, D Basak RSC Advances 4 (102), 58553-58558.
14. Defect controlled ultra high ultraviolet photocurrent gain in Cu-doped ZnO nanorod arrays: De-trapping yield, S Sarkar, D Basak Applied Physics Letters 103 (4), 041112
15. The reduction of graphene oxide by zinc powder to produce a zinc oxide-reduced graphene oxide hybrid and its superior photocatalytic activity, S Sarkar, D Basak Chemical Physics Letters 561, 125-130
16. One-step nano-engineering of dispersed Ag–ZnO nanoparticles’ hybrid in reduced graphene oxide matrix and its superior photocatalytic property, S Sarkar, D Basak CrystEngComm 15 (37), 7606-7614
17. Synthesis of dense intersecting branched tree-like ZnO nanostructures and its superior LPG sensing property, S Sarkar, D Basak Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 176, 374-378.
18. ZnO/graphene quantum dot solid-state solar cell, M Dutta, S Sarkar, T Ghosh, D Basak The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 116 (38), 20127-20131
19. Extraordinarily high ultraviolet photosensitivity and sharp cut off wavelength of hydrothermally grown zinc oxide nanorods, S Sarkar, D Basak AIP Conference Proceedings 1447 (1), 359-360
20. Metal-free doping process to enhance the conductivity of zinc oxide nanorods retaining the transparency, S Panigrahi, S Sarkar, D Basak ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 4 (5), 2709-2716
21. A low temperature in situ facile technique to enhance ultraviolet emission of zinc oxide nanorods and its mechanistic insights, S Sarkar, D Basak Chemical Physics Letters 516 (4-6), 192-198
Dr Anupam Debangshi
1. Ultra Narrow PbS Nanorod Field Emitter, A. Debangshi, U. Thupakula, J. K. Bal, A. H. Khan, A. Dalui, S. Acharya, Journal of Physical Chemistry C 116, 18564 (2012).
2. Evolution of Long Range Bandgap Tunable Lead Sulfide Nanocrystals with Photovoltaic Properties, A. Debangshi, A. H. Khan, U. Thupakula, A. Dalui, S. Maji, S. Acharya, Journal of Physical Chemistry C 117, 7934 (2013).
3. Current Rectification by a Single ZnS Nanorod Probed Using a Scanning Tunneling Microscopic Technique, A. Debangshi, U.Thupakula, J. K. Bal, A. Dalui, D. D. Sarma, S. Acharya, Journal of Materials Chemistry C 2, 1158 (2013).
4. Shape Dependent Synthesis and Field Emission Induced Rectification in Single ZnS Nanocrystals, A. Debangshi, U. Thupakula, A. Dalui, J. K. Bal, G. S. Kumar, S. Acharya, ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 6, 7856 (2014).
5. Probing Local Electronic Structures of Au–PbS Metal–Semiconductor Nanodumbbells, A. Debangshi, U. Thupakula, A H. Khan, G. S. Kumar, P. K. Sarkar, and S. Acharya, ACS Applied Nano Materials 1, 5, 2104–2111.
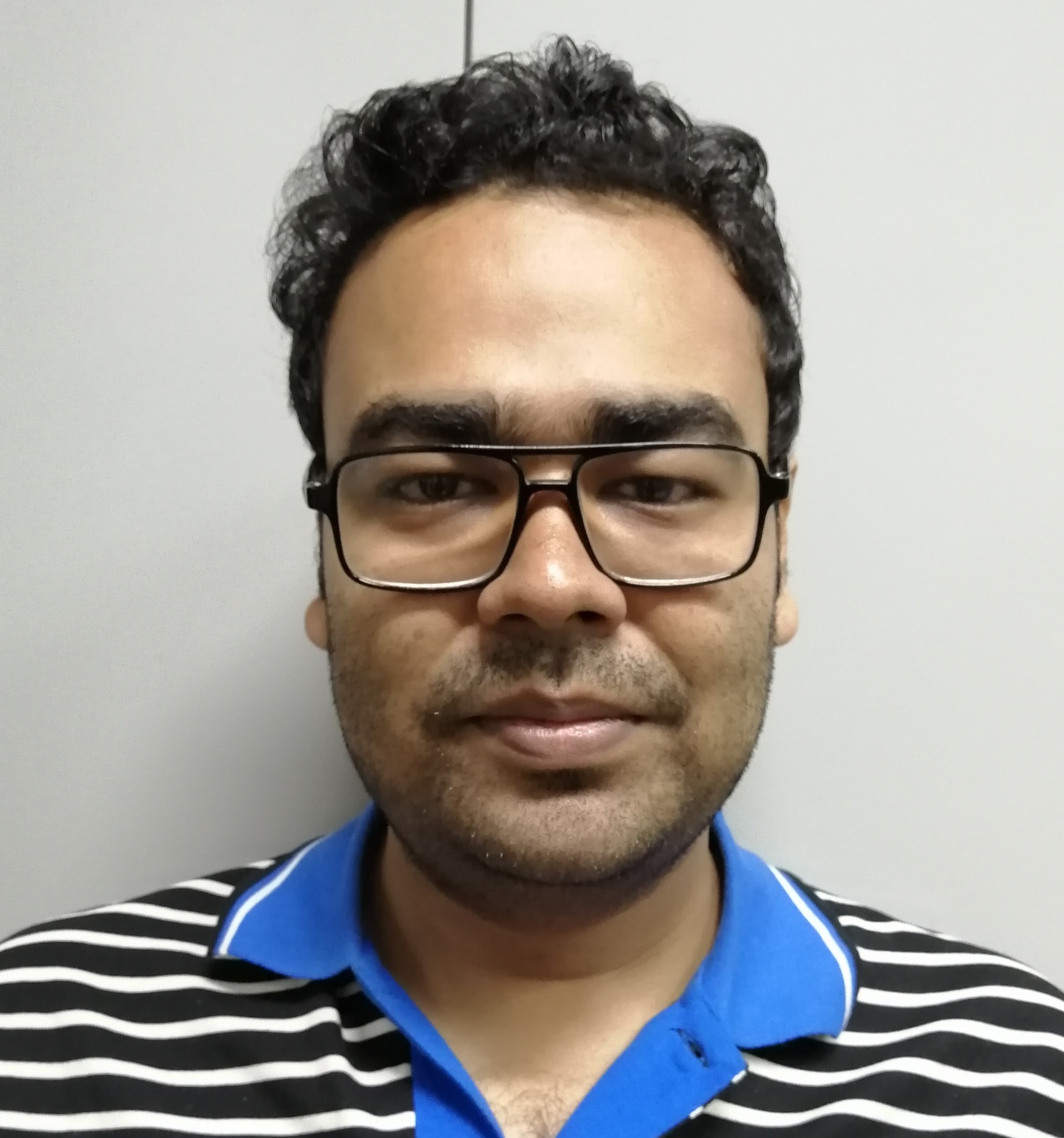
Mr Abdul Lahil Safi
1. CrI3 monolayer: magnetic and electronic behaviors under biaxial strain and external electric field—a first principle study. AL Safi, MA Ahmed – The European Physical Journal B, 2022 – Springer.
2. Tunable electronic, magnetic and optical properties by surface adsorption in monolayer CrI3. AL Safi, MA Ahmed, B Chattopadhyay – Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2024 – Elsevier.
3. Strain tunable electronic band structure and magnetic anisotropy of CrI3 bilayer.. AL Safi, S Chakraborty, MA Ahmed… – ECS Journal of Solid …, 2022 – iopscience.iop.org..
4. WCl3 monolayer: a first principles prediction of electronic and magnetic properties under an external electric field…MA Ahmed, AL Safi – Journal of Computational Electronics, 2024 – Springer..
5. Influence of Mo Doping on Electronic and Magnetic Properties of Monolayer CrX3: A First-Principles Study.. AL Safi, S Chakraborty, MA Ahmed… – ECS Journal of Solid …, 2023 – iopscience.iop.org..
Dr Chirashree Lahiri
1. Recent advances in some nuclear properties relevant to the astrophysical r-process, G. Gangopadhyay and C. Lahiri, Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top., Review article, June (2024).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjs/s11734-024-01215-1
2. Allowed β−decay of bare atoms with A≈60−80 in stellar environments, Arkabrata Gupta, C. Lahiri, and S. Sarkar, Phys. Rev. C 108 (2023) 015805.
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevC.108.015805, (arXiv:2304.00834).
3. Bound and continuum state β − decay of bare atoms: Enhancement of decay rate and changes in β − decay branching, Arkabrata Gupta, C. Lahiri, and S. Sarkar, Phys. Rev. C 100 (2019) 064313.
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevC.100.064313 , (arXiv:1808.09717).
4. Importance of α-induced reactions and the inverse (γ, α) process on p-nuclei, C. Lahiri, Mod. Phys. Lett. A 33 (2019) 1950318.
DOI : 10.1142/S0217732319503188 , (arXiv :1904.01809)
5. Nuclear structure and decay properties of even-even nuclei in Z = 70 − 80 drip-line region, S.Mahapatro, C. Lahiri, Bharat Kumar, R. N. Mishra and S. K. Patra, Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 25 (2016)1650062.
DOI: 10.1142/S0218301316500622 , (arXiv:1512.04665).
6. Modes of decay in neutron-rich nuclei, Bharat Kumar, S. K. Biswal, S. K. Singh, C. Lahiri and S. K. Patra, Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 25 (2016)1650020.
DOI: 10.1142/S0218301316500208, (arXiv:1602.08871 ).
7. Effects of N N potentials on p nuclides in the A∼100-120 region, C. Lahiri and S. K. Biswal and S. K. Patra, Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 25 (2016)1650015.
DOI: 10.1142/S0218301316500154 , (arXiv:1509.04816).
8. Importance of Q-values in astrophysical rp-proces, C. Lahiri and G. Gangopadhyay, Mod. Phys. Lett. A 28 (2013) 1350076.
DOI: 10.1142/S0217732313500764 , (arXiv:1305.6181).
9. Low-energy proton reactions of astrophysical interest in the A≈ 90-100 region, C. Lahiri and G. Gangopadhyay, Phys. Rev. C 86 (2012) 047601.
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevC.86.047601 , (arXiv:1209.2792) .
10. Endpoint of rp process using relativistic mean field approach and a new mass formula, C. Lahiri and G. Gangopadhyay, Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 21 (2012)1250074.
DOI: 10.1142/S0218301312500747 , (arXiv: 1207.2924) .
11. Neutron rich nuclei in a new binding energy formula and the astrophysical r- process, C. Lahiri and G. Gangopadhyay, Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 21 (2012)1250042.
DOI: 10.1142/S0218301312500425 , (arXiv:1207.2937) .
12. Relativistic Mean Field in A∼80 nuclei and low energy proton reactions, C. Lahiri and G. Gangopadhyay, Phys. Rev. C 84 (2011) 057601.
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevC.84.057601, (arXiv:1110.6088).
13. Proton dripline in a new formula for nuclear binding energy, C. Lahiri and G. Gangopadhyay, Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 20 (2011) 2417.
DOI: 10.1142/S0218301311020411 , (arXiv:1110.6093).
14. Microscopic optical model and bridging the waiting points in rp process, C. Lahiri and G. Gangopadhyay, Eur. Phys. J. A 47 (2011) 87.
DOI: 10.1140/epja/i2011-11087-2 , (arXiv:1107.4409).
15. Energy levels in 141Nd from fusion evaporation study, Samit Bhowal, C. Lahiri, Rajarshi Raut, Purnima Singh, M. Kumar Raju, A. Goswami, A.K. Singh, S. Bhattacharya, T. Bhattacharjee, G. Mukherjee, S. Bhattacharyya, S. Muralithar, R.K. Bhowmik, N. Madhavan, R.P.Singh and G. Gangopadhyay, Phys. G: Part. Nucl. Phys 38 (2011).
DOI: 10.1088/0954-3899/38/3/035105.
16. Radiation environment in low energy accelerator for astrophysical studies, Maitreyee Nandy, C. Lahiri , P. K. Sarkar, Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics 48 (2010) 478.
Add-on courses:
1. Household electronics – Basics and Applications
Webinar:























